STRUCTURAL STRENGTHENING, TYFO® SYSTEM
OVERVIEW
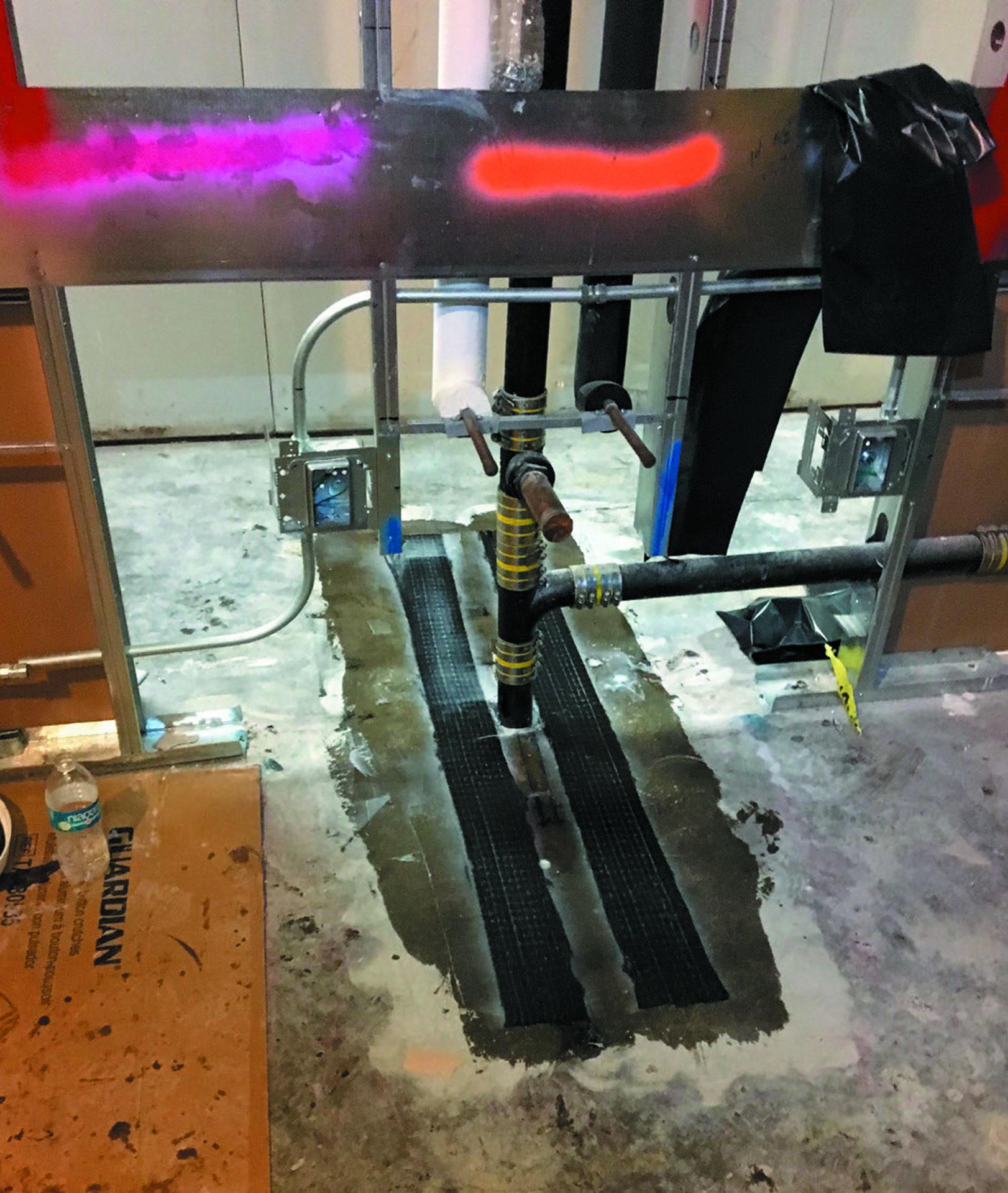
The 2016 modernization project for the NAVFAC Branch Health Clinic in Kings Bay consisted of installing a new plumbing and HVAC systems throughout the facility. The project included the installation of 50 conduits through an elevated floor slab, requiring the contractor to core through the elevated floor slab. Core sizes ranged in diameter from 3 to 10 inches. During the coring process, grade 60 #4 reinforcing steel was damaged at 43 of the coring locations. The 50 cores would significantly reduce the overall strength of the elevated floor slab, requiring strengthening of the slab.
NAVFAC operations used Fyfe Company and its engineer staff to design and run various calculations for different strengthening orientations. The final design called for strengthening of the floor slab. The fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composite system takes advantage of the high strength of woven carbon and glass fibers to provide a much smaller footprint than strengthening with an equivalent design using steel.


A Fyfe® system certified applicator was contracted to install the FRP solution to replace lost strength in the elevated slab due to the reinforcing steel being damaged. The Tyfo® system was chosen as the FRP solution of choice because of the installation speed and overall minimal invasive nature of installation.
The Fyfe® certified applicator used Fyfe Co.’s Tyfo® SCH-41 system to provide the structural equivalent to the grade 60 #4 reinforcing steel in the same orientation as the damage bars.
PROJECT DETAILS
Project NAVFAC Branch Health Clinic Modernization, Concrete slab strengthening.
Location Kings Bay, Georgia
Installation Method Wet lay up
Owner Navy